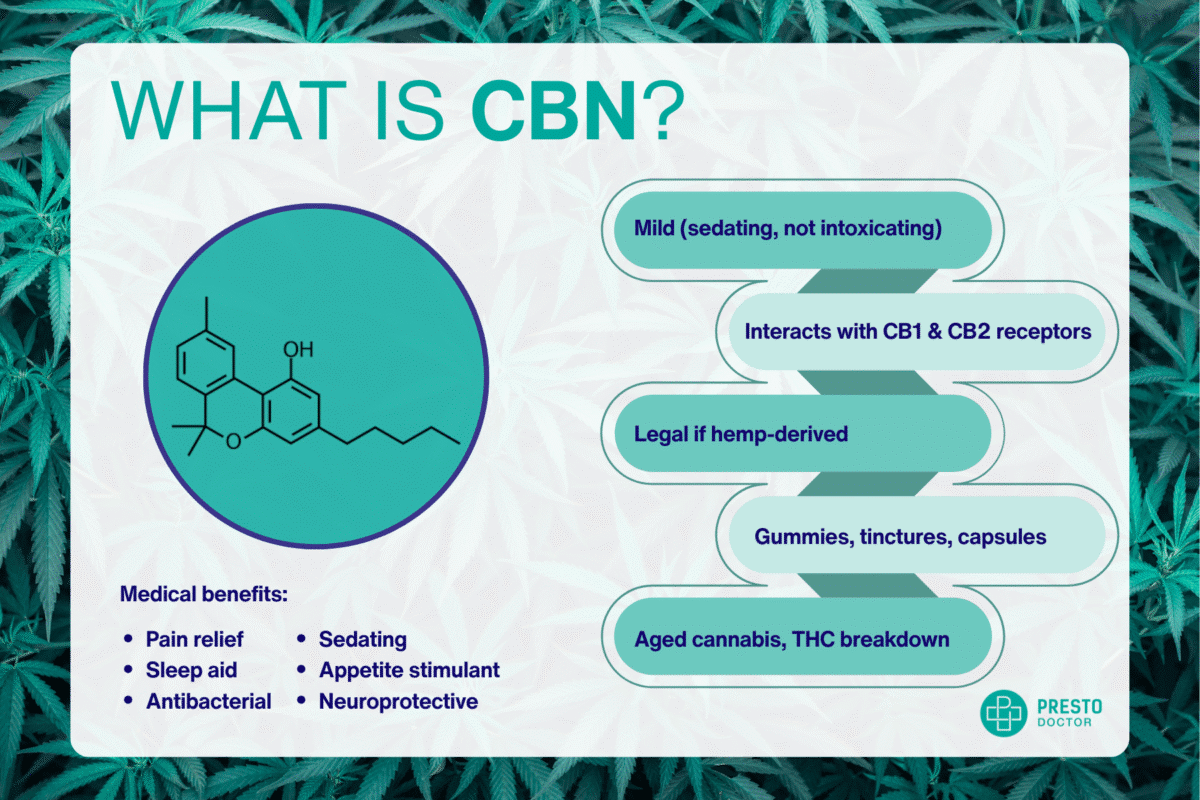
What is Cannabinol (CBN)?
Cannabinol (CBN) is a minor cannabinoid found in cannabis that forms when THC breaks down over time due to exposure to heat, light, or air. Unlike THC, CBN is only mildly psychoactive and is primarily known for its calming, therapeutic effects rather than producing a “high.”
CBN is often found in aged cannabis flower, hash, and specially processed products. Many cannabis users discover CBN effects when using older marijuana that has been exposed to air and light.
CBN in weed typically appears in higher concentrations in aged or improperly stored cannabis, making it a natural byproduct of THC degradation. This unique cannabinoid is gaining attention for its potential benefits in relaxation, pain relief, and wellness applications.
Quick Facts About CBN in Cannabis:
- What it is: A cannabinoid that forms as THC degrades
- Effects: Mildly psychoactive, primarily calming and therapeutic
- Common uses: Relaxation, pain relief, sleep support, wellness
- Legal status: Hemp-derived CBN (under 0.3% THC) is federally legal in the US
- Where it’s found: Higher in aged cannabis flower, hash, and older marijuana products
How CBN Forms in Cannabis
CBN doesn’t naturally occur in fresh cannabis plants. Instead, it develops through a process called oxidation:
- THC exposure: When THC in cannabis is exposed to heat, light, or air over time
- Chemical breakdown: THC molecules gradually convert into CBN
- Higher concentrations: Older, aged, or improperly stored cannabis contains more CBN
- Natural process: This conversion happens naturally but can be accelerated through controlled conditions
This is why aged cannabis flower or hash often produces more relaxing, less intoxicating effects compared to fresh cannabis.
How CBN Interacts with the Endocannabinoid System
CBN interacts with the body’s endocannabinoid system (ECS), which helps with symptom management, wellness, relaxation, pain, inflammation, and immune responses.
CB2 receptor targeting: CBN primarily binds to CB2 receptors in immune cells and peripheral tissues, producing gentle, non-intoxicating effects such as reduced inflammation and muscle relaxation.
CB1 receptors: Weak binding to CB1 receptors may contribute to mild psychoactive and pain-relieving properties
Long half-life: CBN has a longer half-life than many cannabinoids, potentially providing sustained effects
What Does CBN Feel Like?
Users typically describe CBN effects as:
- Gentle body relaxation without mental fog
- Mild sedation similar to chamomile tea
- Subtle pain relief and muscle tension reduction
- Calming sensation without the “high” of THC
- Effects that build gradually and last 4-6 hours
CBN in Weed vs CBD vs THC: Effects and Differences
| Comparison | CBN | THC | CBD |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Relaxation, mild sedation, therapeutic support | Sedation, euphoria | Anxiety relief, inflammation, daytime relaxation |
| Psychoactivity | Mildly psychoactive but mostly non-intoxicating | Psychoactive, can cause a “high” | Non-psychoactive |
| Mode of Use | Often taken alone or combined with indica | Used as a strain of cannabis | Used as oil, tincture, gummies, etc. |
| Best Time to Use | Varies based on intended effect, from relaxation to symptom management | Nighttime or whenever sedation is desired | Daytime or anytime for calming effects |
| Combination Benefit | Can be combined with THC or CBD for enhanced effects | Can be combined with CBN for increased benefits | Combining with CBN covers multiple symptoms |
CBN is unique because it forms as THC degrades, so older or improperly stored cannabis tends to have higher CBN levels. It occupies a special niche among cannabinoids, offering therapeutic effects with less intoxication.
How is CBN different from CBD?
CBN is mildly psychoactive and primarily used for relaxation and sleep, while CBD is non-psychoactive and commonly used for anxiety and inflammation. CBN forms from THC degradation, while CBD occurs naturally in cannabis plants.
Therapeutic Benefits of CBN (Pain, Relaxation, and Wellness)
Currently, researchers are looking into potential health and wellness benefits such as:
- Pain Relief: Reduces inflammation and muscle tension, potentially helping conditions like arthritis or fibromyalgia. CBN in cannabis may be particularly effective for nighttime pain management, as its sedating properties complement its analgesic effects.
- Relaxation & Symptom Management: Promotes calmness without intoxication.
- Neuroprotection: Potential to protect brain cells from oxidative stress.
- Appetite Stimulation: Could assist in appetite regulation, specifically useful in chemotherapy or eating disorders.
These properties make it a potential component in future cannabinoid-based therapies.
Does CBN Enhance THC’s Effects?
CBN may work synergistically with THC through the “entourage effect”, where cannabinoids enhance each other’s benefits. Combining the two can create a more relaxed, balanced experience, while potentially reducing unwanted side effects like paranoia. This makes it appealing for people seeking the calming body effects of cannabis without overwhelming psychoactivity.
Terpenes like myrcene and linalool, found in cannabis alongside CBN, also add calming, sedative effects.
Common CBN Products and How to Use Them
Gummies
- Pros: Convenient, consistent dosing, discreet
- Cons: Slower onset (45–60 minutes)
- Best for: Daily wellness, sleep support
Oils and Tinctures
- Pros: Precise dosing, faster absorption (10–20 minutes)
- Cons: Taste may be unpleasant
- Best for: Microdosing, customizable effects
Capsules
- Pros: Consistent dosing, no taste
- Cons: Slower onset, less flexibility
- Best for: Daily supplementation
Flower and Vapes
- Pros: Rapid effects (5–10 minutes), higher bioavailability
- Cons: Inhalation risks, effects wear off faster
- Best for: Immediate relief, experienced users
Pro tip: Always choose third-party lab-tested products with clear content labeling to ensure quality and safety.
How Much to Take?
There’s no universal dose. Recommendations vary by individual response and also intended use:
| Method | Suggested Dose |
|---|---|
| Clinical research (2024) | 20 mg daily |
| Industry guidelines | Start with 2.5–10 mg, increase gradually |
| Weight-based approach | ~0.1 mg per pound of body weight |
Dosage tips:
- Start with the lowest effective dose
- Increase gradually based on comfort and tolerance
- Track your response and adjust accordingly
- Consider your experience with other cannabinoids
- Consult healthcare providers for medical use
Legal Status
CBN legality depends on whether it’s hemp-derived (federally legal in the US) or marijuana-derived (subject to state cannabis laws). Always check local regulations before purchasing or using cannabinoid products.
Drug Testing Considerations
Standard drug tests typically do not screen for CBN specifically. However, since many CBN products may contain trace amounts of THC, there is a potential risk of testing positive. Choosing third-party lab-tested, THC-free products can minimize this risk.
Future Potential of CBN in Cannabis Medicine
Researchers are exploring the potential of this cannabinoid in:
- Chronic inflammation management
- Neurodegenerative disease support
- Antibacterial and other therapeutic applications
Challenges include natural variability in CBN content, which can make dosing inconsistent in some cannabis products. Innovations in delivery methods may also improve bioavailability and reliability.
Conclusion
CBN in cannabis is more than a breakdown product of THC—it’s a functional, mildly psychoactive cannabinoid with potential for wellness, symptom management, and pain relief.
For those interested in sleep-specific effects, check out our CBN for Sleep guide.
FAQs
It promotes relaxation, supports wellness, and may also reduce inflammation and pain. Users often report feeling mildly sedated, relaxed, and potentially pain relief. Effects are generally milder and more therapeutic compared to THC.
Possibly. Some users report reduced anxiety, though clinical evidence is limited.
Unlikely, but trace THC could result in a positive test.
Start low (2.5–10 mg) and then adjust based on individual response. Clinical studies show 20 mg daily can be effective for many.
No. Legal status depends on whether it’s hemp- or marijuana-derived and local state laws.
Fresh cannabis contains very little CBN (usually less than 1%). However, aged or improperly stored cannabis can contain 2-10% CBN as THC breaks down over time. Hash and concentrates from older material often have higher CBN concentrations.