Does Marijuana Kill Brain Cells? What Science Really Says
Quick Answer:
No, marijuana does not directly kill brain cells like alcohol or nicotine. However, cannabis can affect and cause effects on how brain cells function—especially in adolescents or heavy, long-term users. Research shows that while THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) alters memory, cognition, and learning, it does not appear to be neurotoxic. Luckily, memory loss caused by marijuana can typically be reversed with quitting and the effects are typically not considered permanent.
At a glance:
- 🚫 Marijuana does not kill brain cells directly
- 🔄 It can impair memory, cognition, and coordination
- 🧠 Adolescent users and heavy long-term users are most at risk
- ✅ Most adult-onset effects are mild and reversible
Introduction: Effects of Cannabis on the Brain
As marijuana becomes more widely legalized, concerns about its long-term impact on brain health are growing. One question dominates the conversation: Does weed kill brain cells?
Scientific research paints a nuanced picture. Unlike alcohol and nicotine, which are proven to cause neuron death, cannabis mainly disrupts brain function rather than destroying cells outright. But factors like age of first use, frequency, and THC potency dramatically shape marijuana’s cognitive impact.
How THC Affects the Brain: A Biological Overview
What Is THC and How Does It Work?
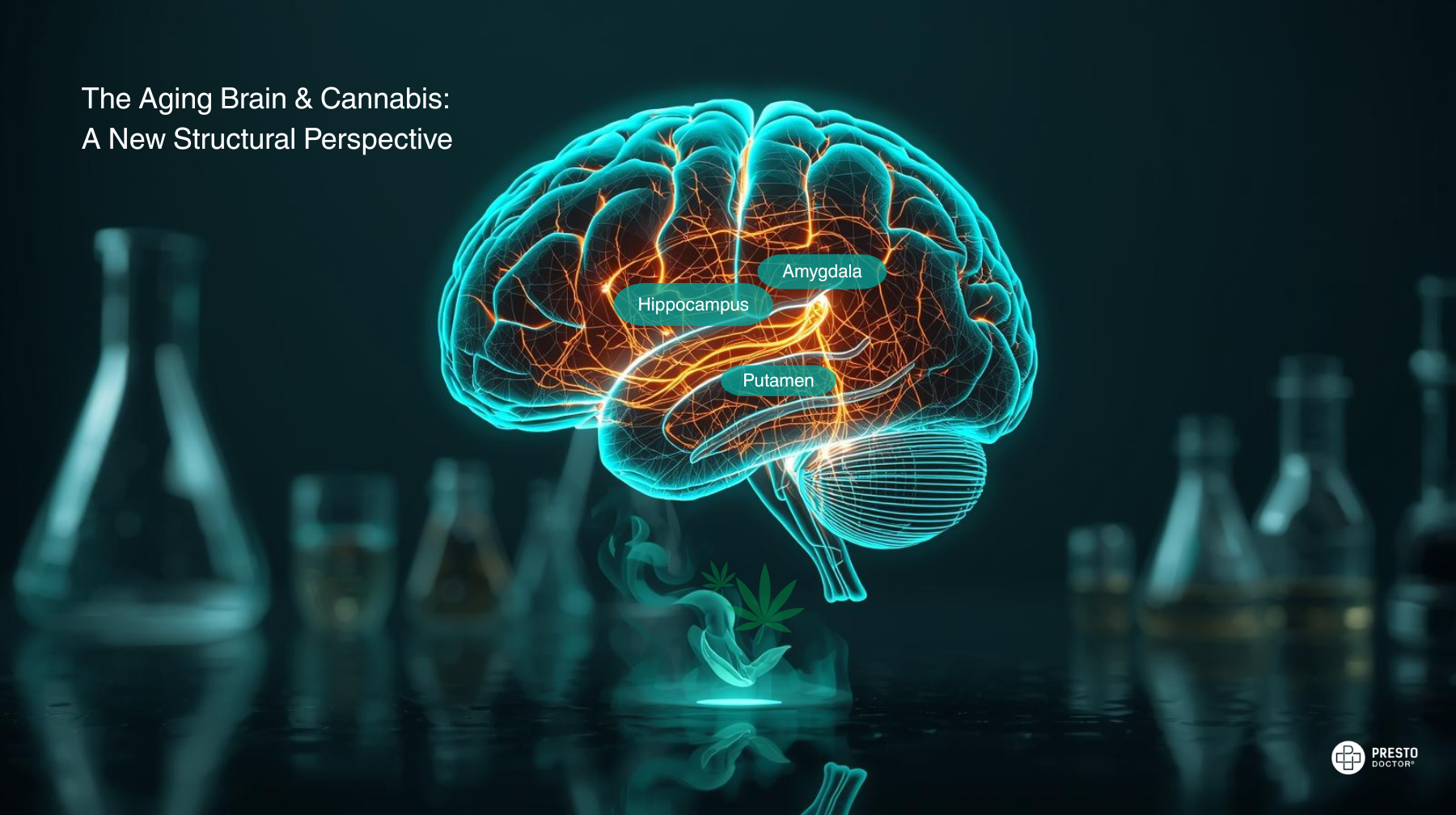
THC binds primarily to CB1 receptors, which are abundant in areas of the brain that control:
- Memory (hippocampus)
- Coordination (cerebellum)
- Executive function (prefrontal cortex)
This interaction alters neurotransmitter signaling, leading to:
- Short-term memory lapses
- Impaired motor skills
- Distorted perception and reaction time
Does Marijuana Kill Brain Cells?
Scientific Analysis
Current evidence suggests that THC does not kill neurons, but it disrupts how they communicate. Unlike methamphetamines or alcohol—which cause cell death through oxidative stress and toxicity—marijuana appears to have more functional than structural effects.
Key Takeaway: Marijuana changes how brain cells work, but doesn’t kill them outright. So the answer is, no weed does not kill brain cells.
Can Marijuana Cause Permanent Brain Damage?
- For adults, the brain is fully developed by age 25, so cognitive changes tend to be milder and often reversible.
- For adolescents, whose brains are still forming, THC can cause:
- Structural changes in gray matter
- Reduced functional connectivity
- Cognitive impairments that may persist into adulthood
Does Marijuana Lower IQ?
The New Zealand Study (2012)
The Dunedin Study tracked over 1,000 people from birth to age 38 and found:
- Adolescent cannabis users lost up to 8 IQ points
- Those who started in adulthood did not show the same decline
Criticisms of the Study:
- IQ was not tested before cannabis use began
- Did not fully control for alcohol use, education, or family background
- IQ decline could be due to other environmental factors
Key Takeaway: Starting cannabis use as a teen may affect IQ. Adult use is much less likely to.
Cannabis and the Adolescent Brain
Absolutely. Marijuana’s impact on the brain is age-dependent:
- Adolescents (under 25): Higher risk of cognitive decline, structural brain changes, and potential for mental health disorders
- Adults (25+): Effects are generally milder and more reversible
Using cannabis during adolescence (before age 18) may disrupt how the brain builds critical connections for attention, memory, and learning—including areas like the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus.
Short-Term Effects of Cannabis on the Brain
- Memory lapses
- Slower reaction time
- Distorted sense of time
- Anxiety or paranoia
- Decreased motor coordination
⏳ These effects usually last 2 to 6 hours depending on dosage and method.
Long-Term Cognitive Effects of Cannabis
Chronic, long-term marijuana use—especially from a young age—can lead to:
- Lower verbal memory performance
- Reduced processing speed
- Executive dysfunction
- Increased risk of developing Cannabis Use Disorder
Emerging research shows that long-term cannabis use may influence how the brain ages, potentially accelerating or modifying age-related cognitive decline.
Marijuana and Memory Loss: What the Research Shows
Cannabis use has been linked to short-term and long-term memory impairments:
- THC affects the hippocampus, impairing short-term recall
- Chronic users may experience long-term memory decline
- Cognitive recovery is possible with abstinence, especially in adults
Key Takeaway: Marijuana can impair memory or cause some memory loss, especially in adolescents and frequent users.
Is Synthetic Marijuana More Dangerous?
Yes. Synthetic cannabinoids like Spice or K2 are far more dangerous than natural THC:
- Bind more aggressively to CB1 receptors
- Linked to seizures, psychosis, cardiac arrest, and death
- Chemically unpredictable and not regulated
Key Takeaway: Synthetic weed is far more dangerous than natural cannabis and should be avoided.
What Are Cannabinoid Receptors and Why Do They Matter?
CB1 and CB2: The Brain’s Cannabis Gateways
The body’s endocannabinoid system contains two primary receptors:
- CB1 receptors – Found mostly in the brain
- CB2 receptors – Found in the immune system
THC binds primarily to CB1, altering how neurons communicate.
Key Takeaway: THC hijacks CB1 receptors in the brain, temporarily disrupting memory and coordination.
Does Smoking Marijuana Kill Brain Cells?
Smoking vs. Edibles: Combustion Risks
- Marijuana smoke contains carbon monoxide, tar, and carcinogens
- These may contribute to oxidative stress and inflammation
- Smoking may pose higher risks than vaporizing or ingesting edibles
Key Takeaway: THC doesn’t kill brain cells, but smoking marijuana may carry added risks from inhaled toxins.
Can Adolescent Marijuana Use Cause Irreversible Cognitive Deficits?
Yes, especially with heavy and early use.
- Impaired memory and IQ
- Disrupted brain development during a critical period
- Long-lasting effects even after quitting
Teens who engage in heavy cannabis use during adolescence often show abnormalities in brain development, including changes to white- and gray-matter structure. Evidence shows that adolescence is a sensitive developmental window, during which cannabis exposure can produce long-term neurocognitive changes. Additionally, cannabis use during adolescence is associated with lower school achievement and greater risk of dropping out of school.
Key Takeaway: Adolescent use poses the greatest risk.
Does Marijuana Affect Brain Development in Babies?
Prenatal exposure may impact:
- Neurogenesis
- Attention and behavior
- Brain wiring during fetal development
Key Takeaway: Pregnant individuals should avoid marijuana use.
How Does Marijuana Compare to Alcohol and Nicotine?
| Substance | Kills Brain Cells? | Cognitive Risk | Adolescent Risk |
|---|---|---|---|
| Marijuana | ❌ Not directly | ⚠️ Moderate | ✅ High |
| Alcohol | ✅ Yes | ✅ High | ✅ High |
| Nicotine | ✅ Yes | ✅ High | ✅ High |
What Is the ABCD Study?
The Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development (ABCD) Study tracks over 11,000 children.
- Cannabis use linked to lower cognitive scores and altered brain connectivity
- Confirms marijuana has age-dependent brain effects
Can Using Weed in Adulthood Cause IQ Loss?
Generally, no.
- Most adult users show no IQ change
- Risk is concentrated in adolescent-onset users
Do THC Edibles Kill Brain Cells?
No. Edibles change how THC is processed but don’t kill brain cells.
- THC converts to 11-hydroxy-THC in the liver
- Effects are more intense and longer lasting
Do Cannabis Concentrates Affect the Brain Differently?
Yes. Concentrates can have 90%+ THC.
- Cause stronger cognitive disruption
- Increase addiction and psychosis risk
Key Takeaway: Concentrates intensify marijuana’s impact.
Can Low Doses of THC Have Positive Effects?
Possibly.
- May help with inflammation, anxiety, and memory in older adults
- Animal studies show improved cognition with microdosing
Does Marijuana Use Cause Psychosis?
In vulnerable individuals—yes.
- Especially with early, heavy use of high-THC strains
- Genetic predisposition increases risk
Can You Recover from the Cognitive Effects of Heavy Marijuana Use?
Yes—especially for adults who abstain.
- Cognitive function can improve within weeks to months
- Some impairments may persist in heavy, early-onset users
Most brain effects appear reversible in adults after quitting cannabis, though residual deficits are possible in those who began use in adolescence.
Does Personal History or Genetics Influence Brain Effects?
Yes. Certain individuals are more vulnerable to marijuana’s cognitive effects:
- Family history of psychosis or schizophrenia
- Genetic traits like COMT gene variation
- Preexisting trauma or mental illness
New findings suggest that marijuana use can trigger epigenetic changes—alterations in gene expression that may influence mental health, memory, and brain development.
What Percentage of THC Is in Modern Cannabis Products?
- 1990s: ~4–5% THC
- Today’s flower: 15–25% THC
- Concentrates: Up to 90% THC
Key Takeaway: Higher potency = increased risks.
Does Marijuana Use Affect Processing Speed?
Yes. Chronic use can lead to:
- Slower mental reaction time
- Decreased ability to multitask or problem-solve
Recovery is likely with abstinence.
Does Marijuana Use Affect Verbal Memory?
Yes, marijuana can impact memory or cause loss. This is one of the most consistently impacted functions.
- Word recall and verbal learning can decline
- Issues more common in daily or early-onset users
Does Marijuana Affect Decision-Making?
Yes. THC can impair the prefrontal cortex, affecting:
- Impulse control
- Long-term planning
- Judgment and risk-taking
Does Long-Term Cannabis Use Increase Dementia Risk?
There is no definitive link, but:
- Some studies suggest THC may disrupt protective processes
- Long-term inflammation and memory loss could increase risk
- More research is needed
What Research Is Ongoing About Weed and Brain Health?
- ABCD Study – Teen brain development
- Human Connectome Project – Brain network mapping
- Longitudinal neuroimaging in cannabis users
- Clinical trials on cannabinoids for PTSD, anxiety, and aging
Key Takeaways
- THC affects brain function but does not directly kill neurons
- Age matters: adolescent brains and those using cannabis during adolescence are more vulnerable
- Memory, decision-making, and IQ are most affected in chronic young users
- Synthetic marijuana is highly dangerous
- Cognitive effects are often reversible in adults
- Low-dose THC may have therapeutic potential
- Marijuana does not kill brain cells
Conclusion: Does Weed Kill Brain Cells?
No, weed doesn’t directly kill brain cells—but it can impair brain function, especially in developing brains. Effects of cannabis on the brain varies widely based on age, dose, frequency, and individual factors.
For most adults using cannabis occasionally, the risks are low. But using cannabis during adolescence, frequent users, and particularly those with mental health vulnerabilities, the risks can be significant and long-lasting. While smoking marijuana does not kill brain cells, individual factors should be taken into consideration.
Understanding the science helps people make informed, responsible choices.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Does weed kill brain cells?
No. It disrupts function but doesn’t kill neurons like alcohol does.
Can marijuana use lower IQ?
Possibly, if use begins in adolescence and is heavy.
Is synthetic weed more dangerous?
Yes. It’s more potent, less predictable, and carries far greater health risks.
Can you recover from cannabis-related cognitive decline?
In many cases, yes—especially in adult users who abstain. In most cases, memory function, including loss, recovers within weeks of quitting marijuana, especially for adult-onset users.
Does marijuana affect mental health?
Yes, especially in those predisposed to anxiety, depression, or psychosis. However, many of the effects of cannabis on the brain can be reversed with quitting.
Does smoking marijuana kill brain cells more than edibles?
Possibly. Smoking introduces harmful chemicals that can stress the brain, while edibles avoid combustion risks.