Tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV) is a lesser-known cannabinoid found in cannabis, primarily in Sativa strains, especially those from Africa. Unlike THC, which is famous for its psychoactive effects, THCV offers unique benefits such as appetite suppression, neuroprotection, and potential therapeutic applications. As research into THCV continues, its distinct profile is gaining attention for its potential to address various health conditions.
What is THCV?
THCV, or Tetrahydrocannabivarin, is a naturally occurring cannabinoid found in cannabis plants. It shares a similar chemical structure to THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) but produces different effects. Primarily found in African Sativa strains such as Durban Poison, THCV typically presents a more energizing and alert high, often making it good for daytime use.
How Does THCV Work?
THCV interacts with the body’s Endocannabinoid System (ECS), binding to cannabinoid receptors CB1 and CB2. Unlike THC, which fully activates the CB1 receptor, THCV acts as a partial agonist, resulting in a milder psychoactive experience. This nuanced interaction means it can both suppress appetite and enhance energy levels, creating a unique profile compared to THC, which typically increases hunger and induces a more sedative state.
Moreover, its distinctive action on the endocannabinoid system contributes to its potential benefits in metabolic regulation and neuroprotection. By stimulating the CB1 receptor only partially, it avoids the intense intoxicating effects commonly associated with THC, making it a promising option for those seeking therapeutic applications without the heavy sedative impact.
Additionally, the compound’s influence on CB2 receptors may support anti-inflammatory responses, further distinguishing it from its psychoactive counterpart. This dual receptor interaction not only highlights its potential for weight management but also opens the door to research into its effects on cognitive health and metabolic disorders.
Effects of THCV on the Endocannabinoid System
The interactions between THCV and the ECS are complex. Its partial activation of CB1 receptors makes it less intoxicating than THC. Additionally, THCV’s effect on CB2 receptors contributes to its potential anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties, offering therapeutic possibilities without causing significant intoxication.
Benefits of THCV
1. Weight Management and Appetite Suppression
One of THCV’s most studied effects is appetite suppression. Unlike THC, which triggers the “munchies,” THCV has been shown to decrease hunger and increase metabolism, making it appealing for those looking to manage weight. Clinical studies have alluded that individuals using THCV reported lower calorie intake and also reduced cravings.
2. Impact on Blood Sugar and Metabolism
In recent studies, THCV has presented improved insulin sensitivity and regulated blood sugar levels, making it potentially useful for managing type 2 diabetes. By promoting better glucose metabolism, it may then help maintain stable blood sugar and reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications.
3. Neuroprotective Properties
Studies suggest that THCV has neuroprotective qualities, helping to reduce oxidative stress and inflammation in the brain. This could make it beneficial for neurodegenerative conditions such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease, where protecting neurons from damage is essential.
THCV-Rich Cannabis Strains
- Durban Poison
- Doug’s Varin
- Pineapple Purps
- Red Congolese
- Jack the Ripper
These strains are primarily Sativa or Sativa-dominant hybrids and are often sourced from African landrace genetics.
Safety and Side Effects of THCV
While generally considered safe, some users may experience mild side effects, including dizziness, dry mouth, or anxiety. As always with any cannabinoid, starting with a low dose and then gradually increasing is best.
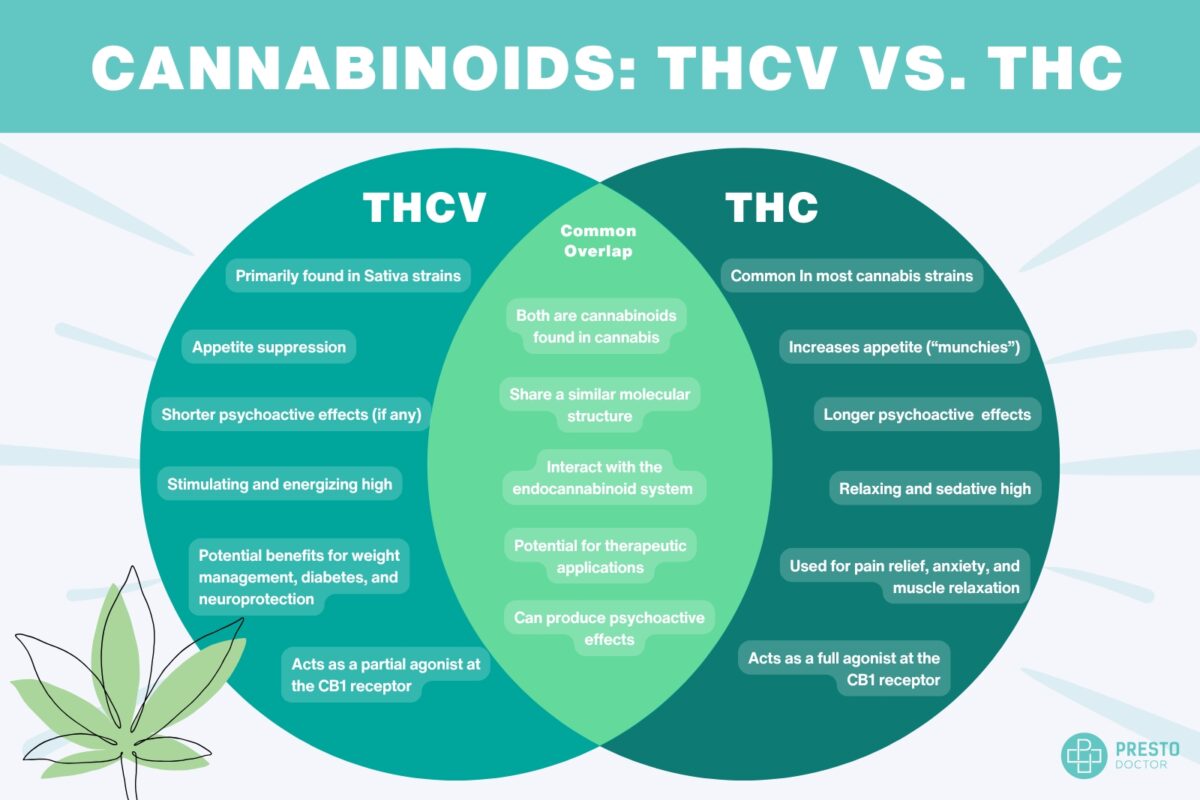
THCV vs THC
Both are cannabinoids that sound similar but have distinct differences in their effects and applications. While both are derivatives from cannabis, their interactions with the endocannabinoid system and their effects on the human body vary significantly.
Psychoactive Properties
- THC is well-known for its psychoactive effects, causing the classic “high” that many users seek.
- THCV, on the other hand, can be psychoactive in high doses, but its effects are generally shorter-lasting and more stimulating rather than sedative.
Appetite and Weight Management
- THC is infamous for triggering the “munchies,” leading to increased appetite.
- THCV does the opposite—it has been shown to suppress appetite and even increase metabolism, making it a potential tool for weight management.
Medical Benefits
- THC is widely used for pain relief, relaxation, and alleviating anxiety.
- THCV is gaining attention for its potential benefits in diabetes management, appetite suppression, and neuroprotection. Some studies also indicate it may help reduce panic attacks without suppressing emotion.
Molecular Structure
Though both cannabinoids have similar molecular structures, a slight difference in the carbon chain makes THCV’s effects distinct. This small variation is responsible for THCV’s unique interactions with CB1 and CB2 receptors.
THCV Gummies
One of the most popular ways to consume is through THCV gummies. These gummies are formulated to deliver precise doses of THCV, therefore making them ideal for beginners and experienced users alike.
Potential Benefits of THCV Gummies
- Appetite Suppression: Perfect for those looking to manage weight without the typical “munchies” associated with THC.
- Neuroprotective Support: May help support brain health, also reducing the risk of cognitive decline.
- Blood Sugar Regulation: Some users take them as a part of their diabetes management plan.
Conclusion
THCV is an intriguing cannabinoid with distinct properties that set it apart from THC. With its potential to aid in weight management, support brain health, and also regulate blood sugar, this cannabinoid holds promise for therapeutic applications. Ongoing research will continue to uncover more about its benefits and optimal usage.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is THCV?
THCV, or Tetrahydrocannabivarin, is a cannabinoid found in cannabis known for its potential to suppress appetite and support brain health.
2. How does THCV work?
THCV interacts with the endocannabinoid system by binding to CB1 and CB2 receptors, but it acts as a partial agonist at CB1, producing unique effects compared to THC.
3. Can THCV help with weight management?
Yes, it has been shown to reduce appetite and increase metabolism, so it makes it a promising candidate for weight management strategies.
4. Are there any side effects of THCV?
Possible side effects include dizziness, dry mouth, and mild anxiety. Always start with a low dose to minimize adverse effects.
5. What are the best THCV-rich strains?
High-THCV strains include Durban Poison, Doug’s Varin, and Pineapple Purps.