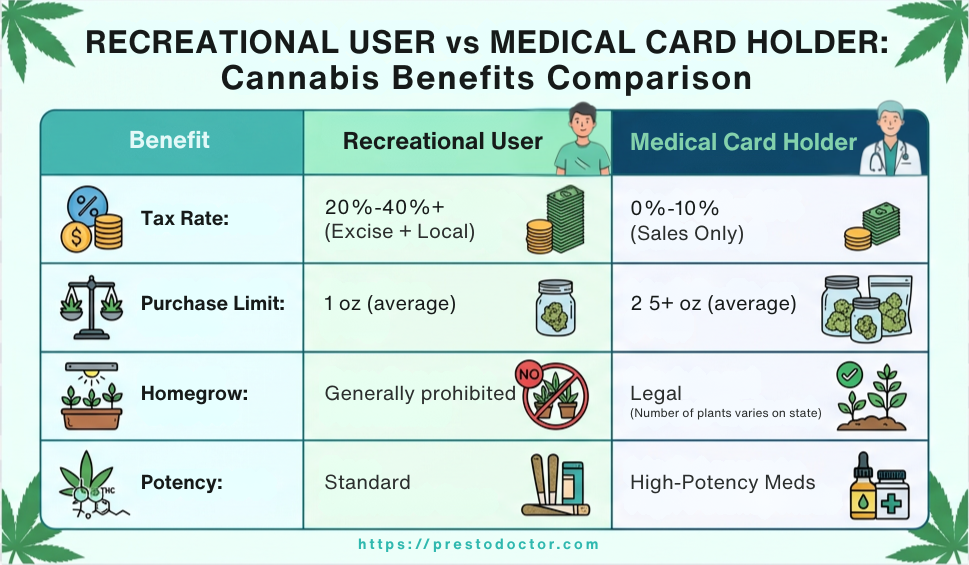
Are you wondering, “How long does THC stay in your pee?” Understanding the duration of marijuana detection in urine is crucial for various reasons, including employment drug screenings, legal matters, and personal health monitoring. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the science behind THC detection in urine and the factors that influence its longevity.
What Stays in Urine?
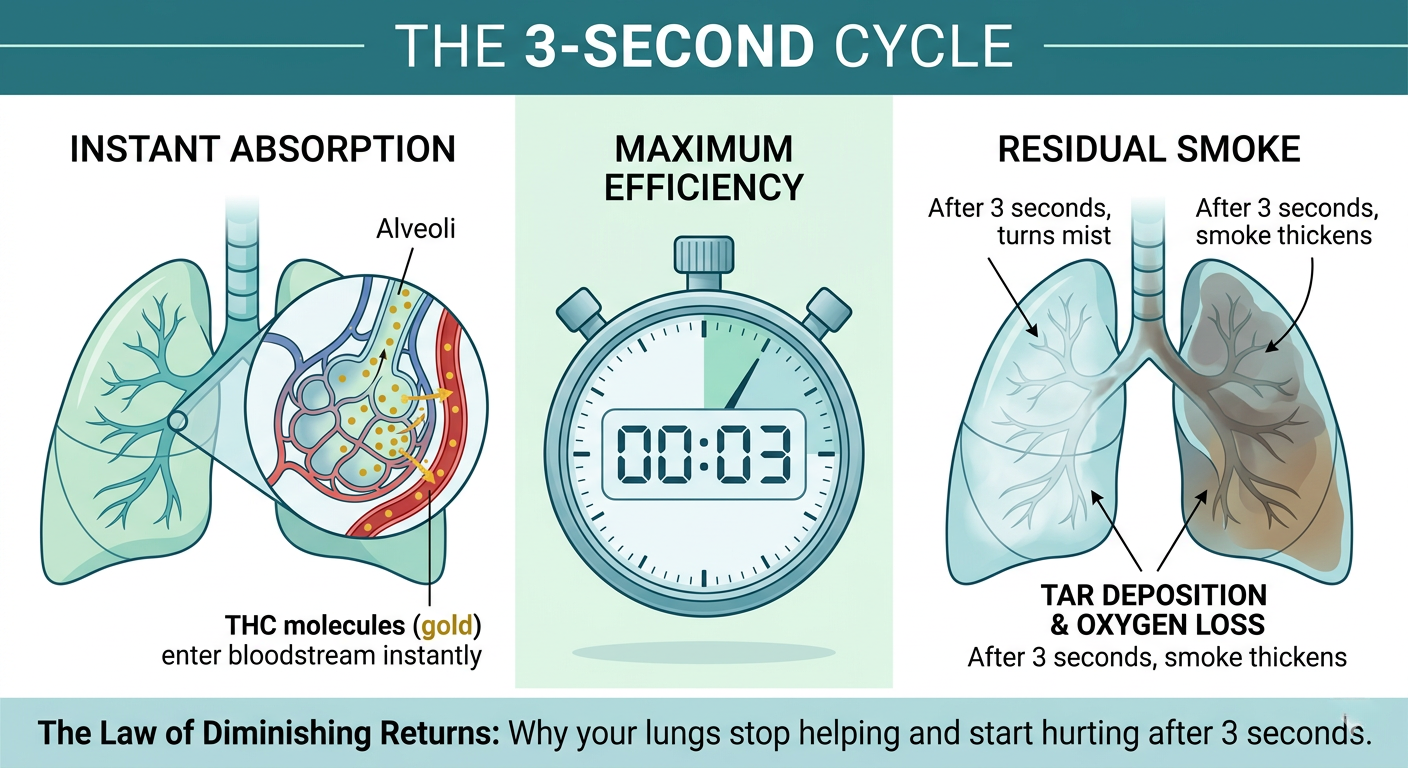
When you consume marijuana, your body metabolizes THC (tetrahydrocannabinol), the primary psychoactive compound, into various metabolites. The most notable metabolite is THC-COOH, which is fat-soluble and can be stored in the body’s fat cells for an extended period. It’s this metabolite that drug tests primarily look for in urine samples.
Detection Timeframe
The duration of THC detection in urine varies significantly among individuals and depends on several factors:
- Frequency of Use: Regular users tend to have THC-COOH stored in their fat cells for longer periods compared to occasional users. Chronic users may test positive for several weeks after cessation, while infrequent users might test negative within days.
- Dosage and Potency: The amount and potency of marijuana consumed also affect detection times. Higher doses and more potent strains can lead to longer detection windows.
- Metabolism and Body Composition: Individual metabolic rates and body fat percentages play crucial roles. Individuals with faster metabolisms and lower body fat percentages may clear THC-COOH more quickly through urine.
- Hydration Levels: Hydration levels can influence urine concentration and the rate at which substances are excreted. Diluted urine may affect the accuracy of drug tests, potentially leading to false negatives.
- Method of Ingestion: The method of marijuana consumption also impacts detection times. Smoking and vaporizing generally lead to shorter detection windows compared to edibles or concentrates.
Detection Methods
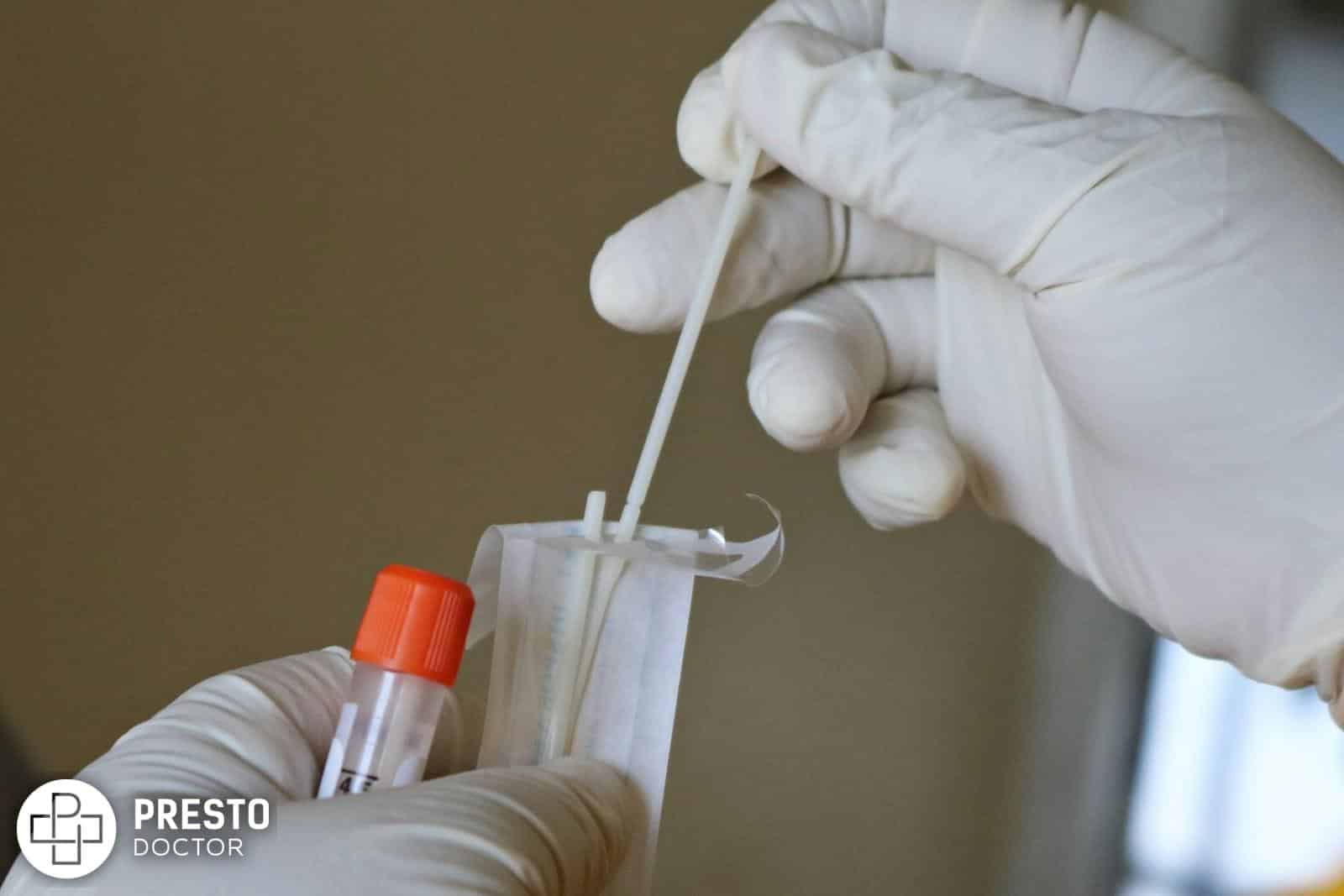
Various drug tests can detect marijuana metabolites in urine, including immunoassay screening tests and confirmatory tests like gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) or high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). Immunoassay tests are rapid and inexpensive but can yield false positives. Confirmatory tests are more accurate and reliable but are typically more expensive and time-consuming.
Conclusion
Understanding how long THC stays in your pee is essential for navigating drug testing scenarios. While general guidelines exist, individual differences can lead to significant variability. Factors such as frequency of use, dosage, metabolism, hydration, and body composition all influence detection times. As research progresses, we can expect more precise methods for detecting marijuana metabolites and a better understanding of how they interact with the body over time. Stay informed to make informed decisions regarding your health and legal obligations.