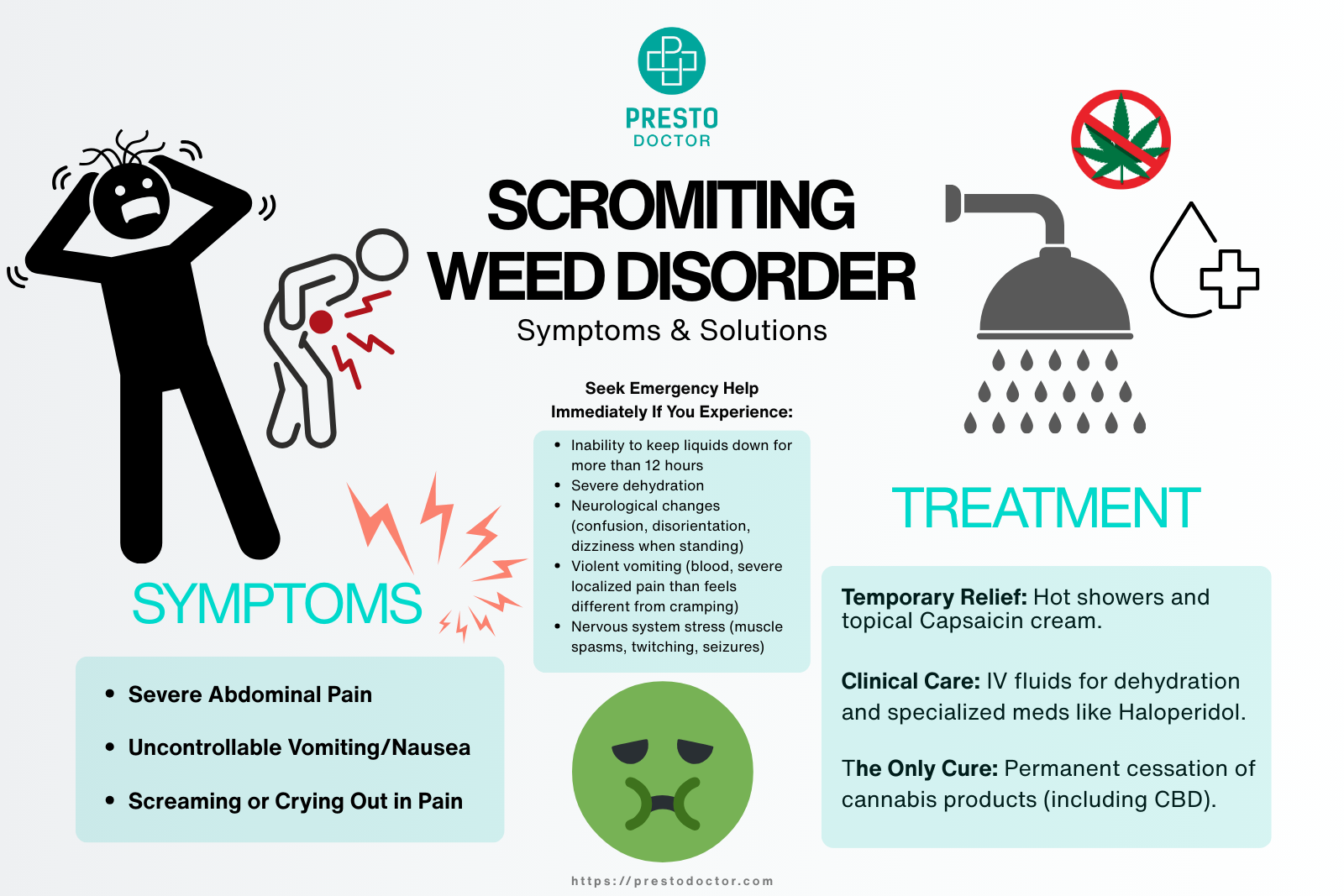
The legalization of cannabis in some countries and states has brought about significant changes in the healthcare industry. One of the most notable shifts is the decrease in the demand for prescription codeine. Codeine is a widely prescribed painkiller that is commonly used to manage mild to moderate pain. However, with the increasing popularity of cannabis, many people are turning to marijuana as a safer and better alternative for pain management. As a result, there has been a significant decline in the use of prescription codeine. In this post, we will discuss the impact of cannabis on prescription codeine and reasons behind this shift in demand. We will also take a closer look at the potential benefits using cannabis as a pain management tool.
Prescription Codeine & Pain Management
Prescription codeine has long played a significant role in pain management. As an opioid medication, it has been used to alleviate moderate to severe pain for decades. Codeine works by binding to opioid receptors in the brain, blocking pain signals and providing a sense of relief.
Traditionally, prescription codeine has been prescribed for a variety of conditions, including post-operative pain, dental procedures, and chronic pain. It has been a go-to option for healthcare professionals seeking to manage pain effectively for their patients. However, with the rise of cannabis, the landscape of pain management is undergoing a notable shift.
Cannabis, particularly strains with high levels of THC, has gained popularity among individuals seeking alternative methods of pain relief. The plant’s active compounds, cannabinoids, interact with the body’s endocannabinoid system, which plays a crucial role in regulating pain perception. This has led many patients to explore cannabis as a potential substitute for prescription codeine.
One of the reasons behind this shift is the concern over the addictive properties and side effects associated with codeine. Opioids, including codeine, have a high potential for abuse and can lead to dependence. Additionally, common side effects such as drowsiness, constipation, and respiratory depression can be burdensome for patients.
In contrast, cannabis is a safer alternative due to its lower risk of addiction and milder side effects. Many users report a reduction in pain and inflammation without experiencing the same degree of sedation or gastrointestinal issues associated with prescription codeine.
The Impact Of Cannabis On Prescription Codeine Demand
The legalization of cannabis has sparked a significant shift in the demand for prescription codeine. As more individuals use cannabis for therapeutic benefits, the need for traditional pain medications like codeine is experiencing a decline.
One of the primary reasons for this shift is the growing acceptance and accessibility of cannabis as an alternative pain management option. Many individuals are now exploring the potential benefits of cannabis for pain relief, inflammation reduction, and relaxation. With the increased availability of cannabis products, individuals are more inclined to give it a try. This is especially true for those seeking a natural and potentially safer alternative to prescription medications.
As more scientific studies emerge, people are becoming more willing to embrace cannabis as a legitimate therapeutic option. This shift has resulted in a decline in demand for prescription codeine, as individuals explore cannabis for pain management needs.
Another factor contributing to the decrease in codeine demand is the potential addictive nature of opioids, including codeine. Many individuals are becoming more cautious about the long-term use of prescription pain medications due to concerns about dependency and the risk of developing opioid use disorder. This has led them to seek out alternative options like cannabis.
The Changing Landscape Of Pain Management
One of the main reasons behind this shift is the perception that cannabis offers a more natural and holistic approach to pain management. Many individuals prefer the idea of using a plant-based substance rather than relying on synthetic pharmaceuticals. Additionally, there is growing anecdotal evidence suggesting that cannabis can be effective in alleviating pain. This makes it an attractive alternative to prescription medications.
- Cannabis as an Analgesic: Cannabis contains various compounds, notably tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD), which have demonstrated analgesic properties. Some patients report relief from chronic pain conditions, such as neuropathy, arthritis, and fibromyalgia, when using cannabis products. This has led to a surge in interest among patients and healthcare providers seeking alternative pain management strategies.
- Reducing Opioid Reliance: One of the most notable effects of cannabis on pain management is its potential to reduce reliance on opioid medications. In regions where medical cannabis is accessible, some studies have shown a decrease in opioid prescriptions and opioid-related fatalities. Patients are exploring cannabis as a less addictive and potentially safer option for pain relief.
Furthermore, the legalization of cannabis in certain jurisdictions has made it more accessible to a wider range of individuals. This increased accessibility has led to a surge in experimentation and exploration of benefits, including its ability to manage pain. As a result, some individuals who would have previously sought out codeine prescriptions may now be turning to cannabis as their preferred method of pain relief.
Research Studies & Evidence On Cannabis & Codeine Use
Research studies and evidence have shed light on the relationship between cannabis and codeine use, providing valuable insights into the impact of cannabis on prescription codeine. These studies have primarily focused on understanding the potential changes in demand for codeine-based medications following the legalization or decriminalization of cannabis in various regions.
- Opioid Use Reduction:
- A study published in the journal JAMA Internal Medicine in 2014 found that states in the United States with medical cannabis laws had a significantly lower rate of opioid overdose deaths compared to states without such laws. This suggests that the availability of medical cannabis may be associated with reduced opioid use, including codeine.
- Substitution Effect:
- Multiple studies have explored the concept of cannabis as a potential substitute for opioids. For example, a study published in the Journal of Pain in 2016 found that chronic pain patients who used medical cannabis reported a decrease in their opioid use and an improved quality of life.
- Another study published in the Journal of Psychoactive Drugs in 2019 indicated that some individuals may turn to cannabis as a substitute for opioids, including codeine, for pain management due to concerns about the addictive nature of opioids.
- Pain Management:
- Research published in the European Journal of Pain in 2018 examined the effects of combining cannabis and opioids for pain management. The study found that patients using both cannabis and opioids reported improved pain relief compared to those using opioids alone. This suggests that some individuals may use cannabis to augment the effectiveness of codeine and other opioids for pain control.
Potential Benefits Of Using Cannabis As An Alternative To Codeine
The benefits of cannabis as an alternative to codeine for pain management have been a subject of increasing interest and research. While it’s essential to consider individual factors and the specific nature of pain conditions, here are some potential benefits associated with using cannabis as an alternative to codeine:
Reduced Risk of Opioid Dependence and Addiction:
One of the most significant benefits of using cannabis as an alternative to codeine is the potential reduction in the risk of opioid dependence and addiction. Codeine, like other opioids, carries a risk of physical and psychological dependence. In contrast, cannabis is generally considered to be less addictive.
Fewer Side Effects:
Cannabis may have fewer side effects compared to opioids like codeine. Opioids can cause constipation, nausea, respiratory depression, and cognitive impairment. Cannabis, especially when using strains with higher CBD content and lower THC content, may result in milder side effects.
Non-Fatal Overdose Risk:
Opioids, including codeine, are associated with a risk of fatal overdose due to respiratory depression. Meanwhile, cannabis has no known fatal overdoses, making it a safer option in this regard.
Versatile Delivery Methods:
Cannabis can be consumed in various forms, including smoking, vaporizing, edibles, oils, and topicals. This versatility allows patients to choose a delivery method that suits their preferences and medical needs.
Broad Spectrum of Pain Relief:
Cannabis has been reported to be effective in managing various types of pain. This includes neuropathic pain, chronic pain, and inflammatory pain. This broad spectrum of pain relief potential may make it a suitable alternative for individuals who do not respond well to codeine or other opioids.
Potential Anti-Inflammatory Effects:
Cannabinoids like CBD have anti-inflammatory properties, which can be beneficial for individuals experiencing pain associated with inflammation. Codeine primarily targets pain perception without addressing the underlying inflammation.
Potential Mood Enhancement:
Some patients using cannabis for pain management have reported improvements in mood and overall well-being. This aspect can be especially relevant for individuals dealing with chronic pain, as it can impact mental health.
Individualized Treatment:
Cannabis allows for a more personalized approach to pain management. Additionally, patients can experiment with different strains and cannabinoid ratios to find the most effective and well-tolerated option for their specific pain condition.
Case Studies: The Impact Of Cannabis On Prescription Codeine Demand
To truly understand the impact of cannabis on prescription codeine demand, examine real-world examples and case studies. These examples provide valuable insights into the shifting patterns of consumer behavior and the potential consequences on the pharmaceutical industry.
The Case of Colorado, USA:
Colorado legalized recreational cannabis in 2014. A study published in JAMA Internal Medicine in 2016 examined the impact of cannabis legalization on opioid prescription rates in the state. The researchers found that after legalization, there was a reduction in opioid prescriptions. This suggests that some individuals may have substituted cannabis for prescription opioids, including codeine, for pain management.
Canada’s Cannabis Legalization:
Canada legalized recreational cannabis in October 2018. Preliminary data from Canada suggests that cannabis legalization has had an impact on the use of prescription opioids, including codeine. Some patients have reported using cannabis to reduce their reliance on opioids for pain management.
Medical Cannabis Access in the United States:
In several U.S. states where medical cannabis programs have been in place for some time, there have also been anecdotal reports of patients with chronic pain conditions using medical cannabis as an adjunct or alternative to prescription opioids, including codeine. These reports suggest that, for some individuals, medical cannabis may offer pain relief without the same risk of dependence.
Qualitative Research:
Qualitative studies involving interviews and focus groups with individuals using both cannabis and prescription opioids have provided insights into their experiences. These studies reveal that some patients perceive cannabis as a more natural and less harmful alternative to opioids for pain management, potentially leading to decreased demand for prescription opioids.
Medical Cannabis Programs and Opioid Reduction Initiatives:
Some healthcare facilities and states in the U.S. have initiated programs that promote the use of medical cannabis as an alternative to opioids, particularly for chronic pain patients. While not specific case studies, these initiatives reflect the growing interest in exploring the impact of cannabis on opioid demand.
It’s essential to note that the relationship between cannabis and prescription codeine demand is complex and multifaceted. Many factors, including individual preferences, medical conditions, and regulatory frameworks, influence this relationship. Moreover, ongoing research is needed to provide more comprehensive and up-to-date insights into how cannabis legalization affects prescription opioid use, including codeine, in different regions. As the field continues to evolve, more case studies and research findings may become available to further inform our understanding of this issue.
These case studies illuminate the potential consequences of legalized cannabis on the demand for prescription codeine.
Evolving Landscape Of Pain Management: Cannabis
As the landscape of pain management continues to evolve, the emergence of cannabis has introduced a new factor to consider. The legalization of cannabis in many regions has sparked significant changes in consumer behavior and preferences, particularly when it comes to pain relief. This shift in demand has had a notable impact on prescription codeine, a commonly prescribed opioid for pain management.
The rise in popularity and acceptance of cannabis has led to a decrease in the demand for prescription codeine. Many individuals are now exploring the potential benefits of cannabis as a means of pain management, opting for a more holistic approach. Moreover, this shift is indicative of a changing mindset and a growing acceptance of alternative methods for addressing pain.
As the era of recreational cannabis unfolds, it is crucial for healthcare providers, policymakers, and individuals alike to stay informed and adapt to these changes. Open and honest discussions about pain management options, including the potential benefits and risks of cannabis, are necessary to ensure the well-being of patients and the responsible use of medication.