Cannabis-derived terpenes (CDTs) are quickly becoming one of the most important topics in cannabis science and product quality, but many consumers still don’t know what makes terpenes from cannabis so different from botanical terpenes. In this 2025 guide, we break down exactly what cannabis-derived terpenes are, the benefits of cannabis terpenes, and how they work alongside cannabinoids according to the latest entourage effect research. We’ll also explain cannabis-derived terpenes vs botanical blends (CDTs vs BDTs), why the difference matters for flavor and effects, and how to read terpene labels so you can choose products based on accurate strain profiles, terpene percentages, and clean lab reports. Whether you’re a new consumer or a seasoned patient, this article gives you everything you need to understand the real therapeutic potential of cannabis terpenes and identify high-quality products based on accurate strain profiles and clean lab reports.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed healthcare professional regarding your personal health or cannabis use. Cannabis laws vary by state; check local regulations before purchasing or consuming cannabis.
Quick Summary
- Cannabis-derived terpenes (CDTs) are natural aromatic compounds extracted from cannabis plants—responsible for each strain’s unique scent, flavor, and are also part of its effect profile.
- They differ from botanical/food-grade terpenes because they retain cannabis-specific minor terpenes, flavonoids, and volatile sulfur compounds (VSCs).
- CDTs may contribute to the entourage effect, potentially influencing relaxation, mood, focus, and also therapeutic benefits.
- Research suggests they may enhance mood, relaxation, and offer anti-inflammatory properties, therefore contributing to the entourage effect.
- Products with 2–8% total terpenes and verified lab results (COAs) are considered ideal for both safety and quality.
What Are Cannabis-Derived Terpenes (CDTs)?
Cannabis-derived terpenes are aromatic oils extracted directly from cannabis flowers. Unlike synthetic or botanical terpenes, CDTs preserve the plant’s full-spectrum chemical fingerprint—including minor terpenes, flavonoids, and even trace sulfur compounds—making them the closest representation of the actual strain. The most compelling entourage effect research shows that cannabinoids and terpenes work synergistically, which is therefore why CDTs are often preferred in full-spectrum products.
These extracts drive not just aroma and flavor, but part of the experience, influencing how relaxing, energizing, or soothing a product may feel.
How CDTs Differ from Botanical Terpenes
One of the most common questions consumers ask is cannabis derived terpenes vs botanical: which is better for flavor and effects? Most vape carts and infused products use botanical terpenes from lavender, lemon peel, or pine. While safe and inexpensive, they cannot replicate the complexity of cannabis.
| Feature | Cannabis-Derived Terpenes | Botanical Terpenes |
|---|---|---|
| Extracted from | Cannabis flowers | Non-cannabis plants |
| Contains trace VSCs | ✔ Yes | ✖ No |
| True strain accuracy | ✔ High | ✖ Moderate |
| Cost to produce | High | Low |
| Flavor authenticity | Strong, complex | Clean but less nuanced |
If a product claims “real strain flavor,” it must list CDTs or cannabis-derived terpenes in the ingredients—not simply “natural terpenes.”
The cannabis derived terpenes vs botanical debate has intensified as new aroma research reveals that VSCs and minor terpenes—found only in CDTs—play a major role in strain authenticity.
2025 Update: The Truth About VSCs (Volatile Sulfur Compounds)
For years, everyone assumed terpenes were 100% responsible for cannabis aroma—but new science proves otherwise.
Recent studies show that the strong “skunky” aroma of strains like Sour Diesel or Garlic Cookies comes from volatile sulfur compounds (VSCs), not just terpenes.
Source: PMC study on VSCs in cannabis aroma
This means only CDTs can accurately preserve the true scent profile of these sulfur-rich strains. Therefore, botanical terpenes cannot replicate this.
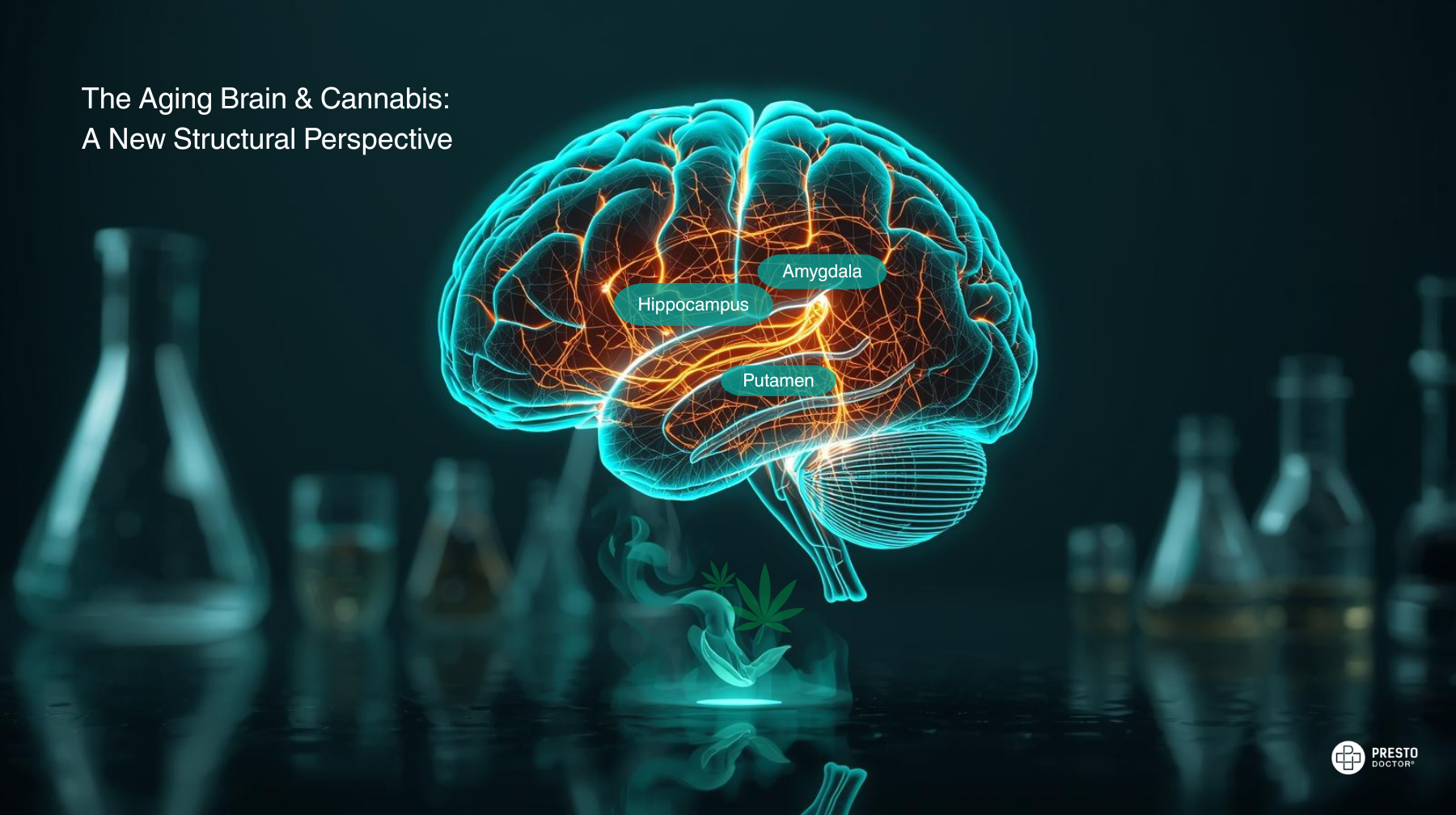
How Terpenes Influence Effects (Backed by Research)
Cannabis researchers now believe terpenes contribute to the entourage effect—the synergistic interaction of cannabinoids and terpenes. Recent entourage effect research suggests that terpenes may modify how THC interacts with the body, contributing to more balanced and also predictable experiences.
According to emerging entourage effect research, terpenes could influence mood, relaxation, and clarity by interacting with:
- GABA receptors
- TRP channels
- Serotonin signaling
Emerging 2025 research has found that some individual terpenes, including linalool and pinene, may act as ‘cannabimimetics,’ meaning they can directly activate CB1 or CB2 receptors—further supporting their potential therapeutic roles in cannabis formulations. Research also suggests that terpenes may enhance effects such as relaxation, mood stabilization, and focus, as seen in studies from the Journal of Psychopharmacology
While these findings are promising, it’s important to emphasize that terpene research is ongoing and most claims reflect early-stage studies rather than definitive clinical conclusions.
It’s also worth noting that the cannabis plant is complex, and in rare cases certain compound combinations can produce antagonistic interactions—sometimes referred to as a ‘contra-entourage effect’—highlighting the importance of precise formulation.
Most Common Cannabis Terpenes (With CDT-Specific Notes)
Understanding the benefits of cannabis terpenes helps consumers choose strains that support relaxation, focus, or mood elevation. Many of the potential therapeutic potential of terpenes, such as calm, anti-inflammatory properties, or enhanced mental clarity, depend on the strain’s dominant terpene profile.
Myrcene (Earthy, Musky, Herbal)
Common in: Granddaddy Purple, Blue Dream
Potential effects: Relaxation, calming, body relief.
Limonene (Lemon, Citrus)
Common in: Lemon Haze, Do-Si-Dos
Potential effects: Mood elevation, stress relief.
Pinene (Pine, Evergreen)
Common in: Sour Diesel, Jack Herer
Potential effects: Focus, alertness, respiratory support.
Caryophyllene (Peppery, Spicy)
Common in: GSC, Chemdawg
Unique feature: Directly interacts with CB2 receptors (rare for terpenes).
Linalool (Lavender, Floral)
Common in: Amnesia Haze, LA Confidential
Potential effects: Relaxation and calm.
Lesser-Known but Important Terpenes (Often Found Only in CDTs)
These are rarely found in botanical blends, which is why CDTs feel more “real.”
Alpha-Bisabolol
Floral, sweet. Found in ACDC, Headband.
Delta-3-Carene
Pine, earthy. May support alertness.
Selinene
Earthy, woody. Contributes to depth in indica strains.
How Terpenes Develop: Cultivation & Post-Harvest Science
How growers increase terpene production:
- UV-B exposure can boost terpene synthesis in trichomes.
- Cooler late-flower temperatures (65–70°F) help preserve volatile terpenes.
- Moderate stress techniques like LST or supercropping can enhance terpene density.
- Organic nutrient regimens improve terpene diversity vs. salt-heavy regimens.
Post-harvest preservation matters even more:
- Drying at 60°F and 60% humidity prevents terpene evaporation.
- Slow curing in airtight containers allows terpenes to stabilize.
- Over-drying destroys up to 40% of the terpene profile.
Storage Tips for Terpene Preservation
- Store terpene-rich products in cool, dark environments (refrigeration is ideal for extracts).
- Avoid frequent temperature swings, which can then cause terpene evaporation.
- Minimize UV exposure, as light breaks down volatile compounds.
- Keep containers fully airtight to prevent oxidation and also the loss of delicate aromatic molecules.
- For vape cartridges, store them upright to keep CDT-rich oils stable.
CDT Extraction Methods
Steam Distillation
Common, but may lose delicate compounds.
Hydrocarbon Extraction (BHO)
Preserves more minor terpenes and VSCs.
Fractional Distillation
Separates terpenes at controlled temperatures—ideal for strain-specific CDTs.
CO₂ Extraction
Clean but can miss certain volatiles unless refined.
When comparing cannabis derived terpenes vs botanical, CDTs consistently provide richer aroma complexity because they preserve cannabis-only compounds that botanicals cannot replicate.
Where CDTs Are Used
CDTs are used in the following products:
- Vape cartridges
- Live resin or rosin pens
- Cannabis beverages
- Edibles
- Pre-roll infusion
- Dab pens & disposables
- Aromatherapy blends
- Tinctures
If a product claims “live,” “fresh frozen,” or “strain-accurate,” it likely uses CDTs.
Are CDTs Safe?
Yes—when:
✔ products use 2–8% total terpene content
✔ terpenes are tested for solvents, pesticides, and heavy metals
✔ they are used in finished products, not applied directly in high concentration
Avoid using highly concentrated, isolated terpenes directly. Look for finished products with terpene percentages in the ideal tested range.
How to Read Terpene Labels
Learning how to read terpene labels is essential for choosing clean, accurately formulated vape carts, flower, and concentrates.
Look for the following:
- Total terpene percentage (2–8%)
- CDT or “cannabis-derived terpenes”
- Strain name
- Extraction method
- COA link
- Batch date
If you’re unsure how to read terpene labels, start by checking the total terpene percentage, the top three dominant terpenes, and whether the product uses cannabis-derived or botanical blends. If you’re looking for the specific benefits of cannabis terpenes, check whether the product highlights CDTs, total terpene percentage, and supporting cannabinoids. Knowing how to read terpene labels helps consumers avoid low-quality or artificially flavored products, especially those lacking verified COAs.
FAQs
Usually yes. CDTs contain cannabis-only compounds like VSCs and minor terpenes, creating stronger aroma and also more strain-accurate effects.
No—terpenes do not produce intoxication. However, they may influence how THC feels through the entourage effect.
Yes, when used in the industry-standard range (2–8%) and tested through a certified lab.
Live resin is a full extract containing cannabinoids + terpenes. CDTs only contain the aromatic fraction.
Final Thoughts
Cannabis-derived terpenes offer a cleaner, more accurate, more flavorful, and often more enjoyable experience than botanical blends. With emerging research revealing the role of VSCs and complex terpene interactions in the body, CDTs continue to lead the future of cannabis flavor science in 2025.